Fast surface immobilization of native proteins through catalyst-free amino-yne click bioconjugation†
Abstract
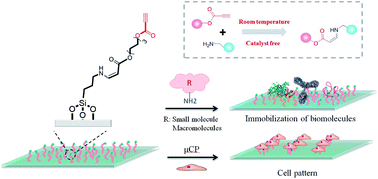
Surface immobilization provides a useful platform for biosensing, drug screening, tissue engineering and other chemical and biological applications. However, some of the used reactions are inefficient and/or complicated, limiting their applications in immobilization. Herein, we use a spontaneous and catalyst-free amino-yne click bioconjugation to generate activated ethynyl group functionalized surfaces for fast immobilization of native proteins and cells. Biomolecules, such as bovine serum albumin (BSA), human IgG and a peptide of C(RGDfK), could be covalently immobilized on the surfaces in as short as 30 min. Notably, the bioactivity of the anchored biomolecules remains intact, which is verified by efficiently capturing target antibodies and cells from the bulk solutions. This strategy represents an alternative for highly efficient surface biofunctionalization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...