Adsorption processes on a Pd monolayer-modified Pt(111) electrode†
Abstract
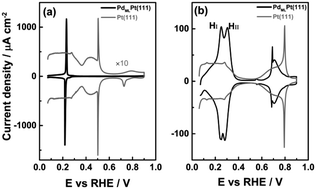
Specific adsorption of anions is an important aspect in surface electrochemistry for its influence on reaction kinetics in either a promoted or inhibited fashion. Perchloric acid is typically considered as an ideal electrolyte for investigating electrocatalytic reactions due to the lack of specific adsorption of the perchlorate anion on several metal electrodes. In this work, cyclic voltammetry and computational methods are combined to investigate the interfacial processes on a Pd monolayer deposited on Pt(111) single crystal electrode in perchloric acid solution. The “hydrogen region” of this PdMLPt(111) surface exhibits two voltammetric peaks: the first “hydrogen peak” at 0.246 VRHE actually involves the replacement of hydrogen by hydroxyl, and the second “hydrogen peak” HII at 0.306 VRHE appears to be the replacement of adsorbed hydroxyl by specific perchlorate adsorption. The two peaks merge into a single peak when a more strongly adsorbed anion, such as sulfate, is involved. Our density functional theory calculations qualitatively support the peak assignment and show that anions generally bind more strongly to the PdMLPt(111) surface than to Pt(111).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...