Photocatalytic hydrogels for removal of organic contaminants from aqueous solution in continuous flow reactors†
Abstract
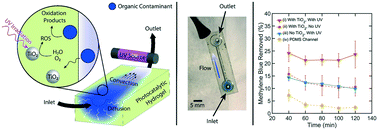
Light-driven degradation of organic contaminants by photocatalytic nanoparticles has attracted significant attention for wastewater treatment applications. However, implementation of these approaches has been limited by challenges in reactor design, which often require post-treatment separation of nanoparticles or exhibit low reactivity owing to immobilization of particles at the surface of heterogeneous supports. In this work, we present a material design strategy that circumvents these challenges by encapsulating photocatalytic particles in three-dimensional polymer networks, leading to structurally-stable photocatalytic hydrogels that were used as the walls of a flow reactor. This design leverages the volumetric reactions of commonly-implemented slurry reactors but circumvents the need for downstream separation of photocatalytic particles. A two-step soft lithography technique was used to fabricate a patterned poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel composite with embedded titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles that were employed as a photocatalyst. In this configuration, contaminant molecules introduced via a flow channel were absorbed into the hydrogel, and subsequently diffused to the surface of the embedded photocatalyst particles where they were oxidized upon light irradiation. Using reactor configurations with low residence times (15 seconds) and moderate UV irradiation (0.28 mW cm−2 at 365 nm), we demonstrated removal of up to 33% of model contaminant methylene blue (MB) and 13% of the antibiotic norfloxacin, both of which were introduced at a concentration of 3 mg L−1. The influence of molecular design parameters, such as hydrogel ionic strength, crosslinking density, and photocatalyst loading on transport and reactor performance were investigated and shown to have a strong influence on the transport properties of the hydrogels, providing options for optimizing the material to enhance treatment efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...