Highly efficient asymmetric reduction of ketopantolactone to d-(−)-pantolactone by Escherichia coli cells expressing recombinant conjugated polyketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase in a fed-batch biphasic reaction system†
Abstract
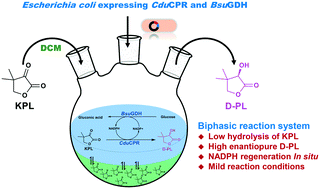
D-(−)-Pantolactone (D-PL) is the key chiral intermediate used to synthesize calcium D-pantothenate. In a previous study, a conjugated polyketone reductase (CduCPR) was discovered to efficiently catalyse ketopantolactone (KPL) to D-PL with a high stereoselectivity. Nevertheless, this method was limited due to the expensive coenzyme, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrate (NADPH), and the poor stability of substrate KPL in pure aqueous buffer. Here, to overcome these problems, we developed a whole-cell biotransformation process to produce D-PL in a biphasic reaction system. Recombinant CduCPR and glucose dehydrogenase (BsuGDH) were co-expressed in Escherichia coli to simultaneously achieve the synthesis of D-PL and the regeneration of NADPH. The biphasic reaction system contained 15% dichloromethane (v/v) which significantly inhibited the undesirable hydrolysis of KPL. Approximately, 2.8% of 100 mM KPL was spontaneously hydrolysed to ketopantoic acid in the biphasic system, which was lower than 54% of pure aqueous buffer. The biphasic reaction system was optimized and scaled up to prepare D-PL. In a fed-batch biphasic reaction, the substrate KPL was continuously fed into the reactor after a batch reaction. The D-PL concentration reached 0.77 mol L−1 in the reaction mixture at 7 h, and its enantiomeric excess was 99%. This study presented an alternative method to asymmetrically synthesize enantiopure D-PL for further industrial application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...