Microfluidic immobilized enzyme reactors for continuous biocatalysis
Abstract
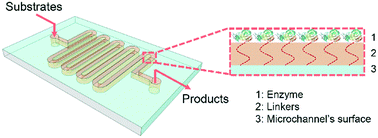
Biocatalysis has attracted significant attention owing to its environmental-friendly nature, high efficiency, and remarkable selectivity for reactions. However, enzymes, which are powerful catalysts used in biocatalysis, suffer from low stability when used for long-term operations in solution and a gradual decrease in activity during storage. Microfluidic reactors are devices known for their smaller dimensions, large surface-to-volume ratios, and well-defined reaction times. Enzymes immobilized in such microfluidic reactors can exhibit distinct benefits, such as fast reaction rate, high storage stability, suppressed autolysis, and ease of use. The use of microfluidic immobilized enzyme reactors (μ-IMERs) offers several advantages over traditional technologies in performing biocatalytic reactions, such as low energy consumption, rapid heat exchange, fast mass transfer, high efficiency, and superior repeatability. In this review, the strategies of employing μ-IMERs for continuous biocatalysis have been investigated via a top-down approach. First, from the macroscopic perspective, the fabrication techniques of microfluidic reactors are presented encompassing materials, configurations, and technologies. Then, from the microscopic point of view, several strategies are discussed for the internal structural designs of microfluidic reactors. Moreover, when we move to the nanoscopic level, attention is paid to the choice of enzyme immobilization techniques for performance enhancement. Finally, the scalability of microfluidics that transfers biocatalysis from laboratory to industrial production was investigated. This review is intended to provide a guideline for using biocatalysis in microreactors and expediting the progress of this important research area.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...