Lipid membrane interactions of self-assembling antimicrobial nanofibers: effect of PEGylation†
Abstract
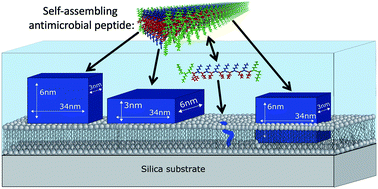
Supramolecular assembly and PEGylation (attachment of a polyethylene glycol polymer chain) of peptides can be an effective strategy to develop antimicrobial peptides with increased stability, antimicrobial efficacy and hemocompatibility. However, how the self-assembly properties and PEGylation affect their lipid membrane interaction is still an unanswered question. In this work, we use state-of-the-art small angle X-ray and neutron scattering (SAXS/SANS) together with neutron reflectometry (NR) to study the membrane interaction of a series of multidomain peptides, with and without PEGylation, known to self-assemble into nanofibers. Our approach allows us to study both how the structure of the peptide and the membrane are affected by the peptide–lipid interactions. When comparing self-assembled peptides with monomeric peptides that are not able to undergo assembly due to shorter chain length, we found that the nanofibers interact more strongly with the membrane. They were found to insert into the core of the membrane as well as to absorb as intact fibres on the surface. Based on the presented results, PEGylation of the multidomain peptides leads to a slight net decrease in the membrane interaction, while the distribution of the peptide at the interface is similar to the non-PEGylated peptides. Based on the structural information, we showed that nanofibers were partially disrupted upon interaction with phospholipid membranes. This is in contrast with the considerable physical stability of the peptide in solution, which is desirable for an extended in vivo circulation time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...