Two decades of recent advances of Ugi reactions: synthetic and pharmaceutical applications
Abstract
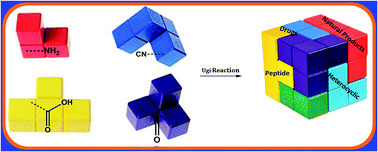
Multicomponent reactions (MCRs) are powerful synthetic tools in which more than two starting materials couple with each other to form multi-functionalized compounds in a one-pot process, the so-called “tandem”, “domino” or “cascade” reaction, or utilizing an additional step without changing the solvent, the so-called a sequential-addition procedure, to limit the number of synthetic steps, while increasing the complexity and the molecular diversity, which are highly step-economical reactions. The Ugi reaction, one of the most common multicomponent reactions, has recently fascinated chemists with the high diversity brought by its four- or three-component-based isonitrile. The Ugi reaction has been introduced in organic synthesis as a novel, efficient and useful tool for the preparation of libraries of multifunctional peptides, natural products, and heterocyclic compounds with stereochemistry control. In this review, we highlight the recent advances of the Ugi reaction in the last two decades from 2000–2019, mainly in the synthesis of linear or cyclic peptides, heterocyclic compounds with versatile ring sizes, and natural products, as well as the enantioselective Ugi reactions. Meanwhile, the applications of these compounds in pharmaceutical trials are also discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...