In situ synthesis of copper nanoparticles encapsulated by nitrogen-doped graphene at room temperature via solution plasma†
Abstract
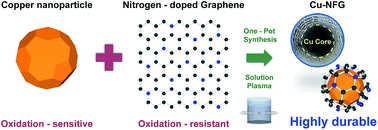
Metal–carbon core–shell nanostructures have gained research interest due to their better performances in not only stability but also other properties, such as catalytic, optical, and electrical properties. However, they are limited by complicated synthesis approaches. Therefore, the development of a simple method for the synthesis of metal–carbon core–shell nanostructures is of great significance. In this work, a novel Cu–core encapsulated by a N-doped few-layer graphene shell was successfully synthesized in a one-pot in-liquid plasma discharge, so-called solution plasma (SP), to our knowledge for the first time. The synthesis was conducted at room temperature and atmospheric pressure by using a pair of copper electrodes submerged in a DMF solution as the precursor. The core–shell structure of the obtained products was confirmed by HR-TEM, while further insight information was explained from the results of XRD, Raman, and XPS measurements. The obtained Cu-core encapsulated by the N-doped few-layer graphene shell demonstrated relatively high stability in acid media, compared to the commercial bare Cu particles. Moreover, the stability was found to depend on the thickness of the N-doped few-layer graphene shell which can be tuned by adjusting the SP operating conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...