Solute displacement in the aqueous phase of water–NaCl–organic ternary mixtures relevant to solvent-driven water treatment
Abstract
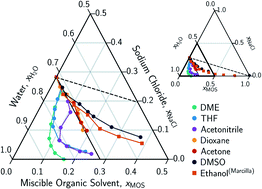
Twelve water miscible organic solvents (MOS): acetone, tetrahydrofuran, isopropanol, acetonitrile, dimethyl sulfoxide, 1,4-dioxane, dimethylacetamide, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, trifluoroethanol, isopropylamine, dimethylformamide, and dimethyl ether (DME) were used to produce ternary mixtures of water–NaCl–MOS relevant to MOS-driven fractional precipitation. The aqueous-phase composition of the ternary mixture at liquid–liquid equilibrium and liquid–solid endpoint was established through quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance and mass balance. The results highlight the importance of considering the hydrated concentrations of salts and suggest that at high salt concentrations and low MOS concentration, the salt concentration is governed by competition between the salt ions and MOS molecules. Under these conditions a LS phase boundary is established, over which one mole of salt is replaced by one mole of MOS (solute displacement). At higher MOS concentrations, MOS with higher water affinity deviate from the one-to-one solute exchange but maintain a LS boundary with a homogenous liquid phase, while MOS with lower water affinity form a liquid–liquid phase boundary. DME is found to function effectively as an MOS for fractional precipitation, precipitating 97.7% of the CaSO4 from a saturated solution, a challenging scalant. DME-driven water softening recycles the DME within the system improving the atom-efficiency over existing seawater desalination pretreatments by avoiding chemical consumption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...