Study of the magnetic interface and its effect in Fe/NiFe bilayers of alternating order†
Abstract
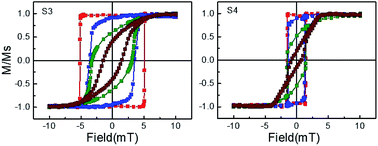
We present a comprehensive study on the magnetization reversal in the Fe/NiFe bilayer system by alternating the order of the magnetic layers. All the samples show growth-induced uniaxial magnetic anisotropy due to the oblique angle deposition technique. Strong interfacial exchange coupling between the Fe and NiFe layers leads to single-phase hysteresis loops in the bilayer system. The strength of coupling being dependent on the interface changes upon alternating the order of magnetic layers. The magnetic parameters such as coercivity HC, and anisotropy field HK become almost doubled when a NiFe layer is grown over the Fe layers. This enhancement in the magnetic parameters is primarily dependent on the increase of the thickness and magnetic moment of the Fe–NiFe interfacial layer as revealed from the polarized neutron reflectivity (PNR) data of the bilayer samples. The difference in the thickness and magnetization of the Fe–NiFe interfacial layer indicates the modification of the microstructure by alternating the order of the magnetic layers of the bilayers. The interfacial magnetic moment increased by almost 18% when the NiFe layer was grown over the Fe layer. In spite of the different values of anisotropy fields and modified interfacial exchange coupling, the Gilbert damping constant values of the ferromagnetic bilayers remain similar to the single NiFe layer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...