Barrier-promoting efficiency of two bioactive flavonols quercetin and myricetin on rat intestinal epithelial (IEC-6) cells via suppressing Rho activation
Abstract
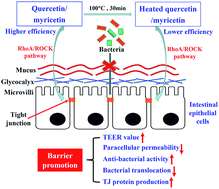
Polyphenols are beneficial to human health because of their bio-activities. In this study, two flavonols quercetin and myricetin with or without heat treatment at 100 °C for 30 min were assessed for their barrier-promoting efficiency in rat intestinal epithelial (IEC-6) cells. The results indicated that the heated and unheated flavonols at dose levels of 2.5–20 μmol L−1 had a nontoxic effect on the cells treated for 24 and 48 h but enhanced the values of cell viability larger than 100% (especially at a dose level of 5 μmol L−1). Moreover, the cells exposed to these flavonols of 5 μmol L−1 for 24 and 48 h had improved barrier integrity compared to the control cells without any flavonol treatment, reflected by enhanced transepithelial electrical resistance and anti-bacterial effect but decreased paracellular permeability and bacterial translocation. Moreover, the results from both mRNA and protein expression verified 1.1–3.4 fold up-regulation of zonula occludens-1, occludin, and claudin-1 that are critical to tight junctions and barrier function of cells. Furthermore, the expression of other two proteins RhoA and ROCK in the treated cells was also down-regulated, demonstrating suppressed Rho activation and consequently barrier promotion via the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Overall quercetin, due to its lower molecular polarity, mostly gave higher barrier-promoting efficiency than myricetin, while the heated flavonols were always less efficient than the unheated counterparts to promote barrier integrity of IEC-6 cells. It is thus highlighted that flavonols can provide barrier-promoting effects on intestinal epithelial cells with a promoting efficiency dependent on flavonol polarity; however, heat treatment especially excessive heat treatment of plant foods might lead to damaged flavonol activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...