Exploring stereoselective excretion and metabolism studies of novel 2-(2-hydroxypropanamido)-5-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid enantiomers
Abstract
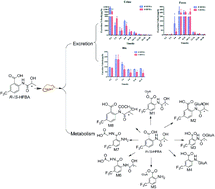
R-/S-2-(2-Hydroxypropanamido)-5-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid (R-/S-HFBA), as a novel COX inhibitor, was firstly reported to have remarkable anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet aggregation activities by our group. In our previous study, stereoselective differences in pharmacokinetics were found between HFBA enantiomers after oral and intravenous administration of each enantiomer to rats. The discrepancies might be associated with the excretion and metabolism of the two enantiomers. In this research, an UHPLC-MS/MS method was established and validated for quantification of R-/S-HFBA in rats urine, feces and bile samples in excretion study. Moreover, an ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (UHPLC-FT-ICR-MS) method was employed to understand the metabolism of R-/S-HFBA in rats. Results showed that the total cumulative excretion of R-/S-HFBA in three routes were 65.8% and 58.5% of the dose, respectively. The urinary excretion of R-/S-HFBA was the main route, which accounted for 40.2% and 31.7% respectively; the cumulative biliary excretion of R-/S-HFBA were 11.3% and 7.4%; the cumulative amounts of R-/S-HFBA excreted directly via feces without absorption from the gastrointestinal tract were 14.3% and 19.4%, respectively. R-/S-HFBA existed stereoselective discrepancy in excretion. In addition, 8 metabolites of S-HFBA were detected and tentatively identified including glucuronidation, glycine and N-acetyl conjugation while R-HFBA existed 7 metabolites without glycine conjugation. Formation of metabolites of R-/S-HFBA also exhibited stereoselectivity. In summary, these new findings on excretion and metabolism of R-/S-HFBA provided valuable information for stereoselective pharmacokinetics and were greatly helpful for further investigation, such as safety and mechanism of action.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...