Structural effect of oxazolone derivatives on the initiating abilities of dye-borate photoredox systems in radical polymerization under visible light†
Abstract
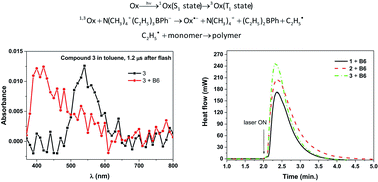
Three photoinitiating systems based on new oxazolone derivatives have been developed and their performance in initiation of radical polymerization of acrylate monomers has been tested by differential scanning calorimetry. The absorption characteristics of the oxazol-5(4H)-ones is compatible with the emission characteristics of different light sources like diode pulse solid state lasers. Thus, the dyes were used as sensitizers which are photoreduced during a photochemical reaction in the presence of phenyltriethylborate salt. Results showed that the increase in the dimensionality of the molecule extends the range of light absorption and increases the efficiency of the photoinitiation process. The photoreduction of the oxazolone–borate complex was studied using steady-state and nanosecond laser flash photolysis. The dye singlet and triplet were found to be quenched by the electron donor via an electron transfer process. Rate constants for the quenching of the excited states were high and were found to depend on the dye structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...