Novel nicotinoid structures for covalent modification of wood: an environmentally friendly way for its protection against insects†‡
Abstract
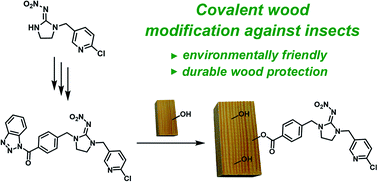
Timber is constantly exposed to environmental influences under outdoor conditions which limits its lifetime and usability. In order to counteract the damaging processes caused by insects, we have developed a novel and more environmentally friendly method to protect wood materials via covalent modification by organic insecticides. Starting with an important class of synthetic insecticides which are derived from the natural insecticide nicotine, various new carboxylic acid derivatives of imidacloprid were made accessible. These activated neonicotinoids were utilized for the chemical modification of wood hydroxy groups. In contrast to conventional wood preservation methods in which biocides are only physically bound to the surface for a limited time, the covalent fixation of the preservative guarantees a permanent effect against wood pests, demonstrated in standardized biological tests. Additionally, the environmental interaction caused by non-bound neonicotinoids is significantly reduced, since both, a smaller application rate is required and leaching of the active ingredient is prevented. By minimizing the pest infestation, the lifetime of the material increases while preserving the natural appearance of the material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...