Cu-based metal–organic framework HKUST-1 as effective catalyst for highly sensitive determination of ascorbic acid
Abstract
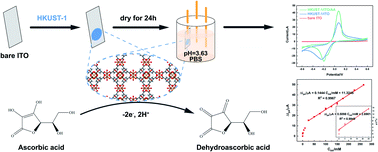
In this work, a Cu-based nanosheet metal–organic framework (MOF), HKUST-1, was synthesised using a solvent method at room temperature. Its morphology, structure and composition were characterised by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherms, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and elemental analysis (EA). This material was then loaded onto the surface of an indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode to catalyse the electrochemical oxidation of ascorbic acid (AA). An equal-electron-equal-proton reaction was deduced from the pH investigation, and a diffusion-controlled process was reinforced by the dynamics study. Under optimal conditions, the oxidation peak current at +0.02 V displayed a linear relationship with the concentration of AA within the ranges of 0.01–25 and 25–265 mM, respectively. The limit of detection (LOD) was 3 μM at S/N of 3. The superb response could be ascribed to the porous nanosheet structure of HKUST-1, which enhanced both the effective surface area and the electron transfer ability significantly. Moreover, the novel AA sensor demonstrated good reproducibility, favourable stability and high sensitivity towards glucose, uric acid (UA), dopamine (DA) and several amino acids. It was also successfully applied to the real sample testing of various AA-containing tablets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...