Screening and characterisation of CdTe/CdS quantum dot-binding peptides for material surface functionalisation†
Abstract
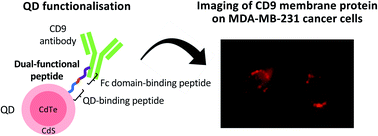
Quantum dots (QDs) are promising nanomaterials due to their unique photophysical properties. For them to be useful in biological applications, the particle surface generally needs to be conjugated to biological molecules, such as antibodies. In this study, we screened CdTe/CdS QD-binding peptides from a phage display library as linkers for simple and bio-friendly QD modification. Among five QD-binding peptide candidates, a series of truncated peptides designed from two high-affinity peptides were subjected to an array-based binding assay with QDs to assess their functional core sequences and characteristics. Linking these isolated, shortened peptides (PWSLNR and SGVYK) with an antibody-binding peptide (NKFRGKYK) created dual-functional peptides that are capable of QD surface functionalisation by antibodies. Consequently, the dual-functional peptides could mediate anti-CD9 antibody functionalisation onto CdTe/CdS QD surface; CD9 protein imaging of cancer cells was also demonstrated. Our proposed peptides offer an effective vehicle for QD surface functionalisation in biological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...