Effects of temperature and polyols on the ciprofloxacin hydrochloride-mediated micellization of sodium dodecyl sulfate†
Abstract
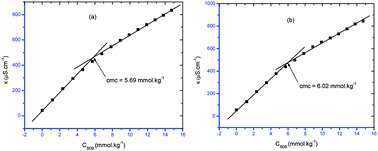
Herein, a conductivity method was engaged to explore the effects of a fluoroquinolone drug, namely ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CFH)/CFH + polyols (organic compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups (glucose and fructose)), on the aggregation phenomenon of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) at different temperatures (298.15–318.15 K) while maintaining a gap of 5 K. In this study, the critical micelle concentration (cmc) of the SDS/SDS + CFH mixture in water and polyols media was determined from plots of the specific conductivity versus the concentration of SDS to gain knowledge of the effects of CFH/CFH + polyols on the micelle formation behavior of SDS. The cmc value of the surfactant decreases in the presence of CFH in an aqueous medium; thus, CFH favors the micellization of SDS. The cmc values of SDS and the SDS + CFH mixture were enhanced in polyols media. The cmc values of SDS/SDS + CFH show a U-shaped behavior with temperature. The counterion dissociation (α) of the pure surfactant is higher in the presence of the drug and is further enhanced through an increase in the CFH concentration in water/polyols media. Different thermodynamic parameters, such as the Gibbs free energy of micellization 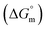 , standard enthalpy
, standard enthalpy 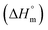 , entropy
, entropy 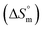 , different transfer energies and enthalpy–entropy compensation parameters of micellization were determined and illustrated in detail to compare these parameters between the pure SDS and SDS + CFH mixture in polyols media. The negative values of
, different transfer energies and enthalpy–entropy compensation parameters of micellization were determined and illustrated in detail to compare these parameters between the pure SDS and SDS + CFH mixture in polyols media. The negative values of 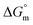 for the SDS/SDS + CFH mixture in all cases indicate spontaneous micelle formation. The
for the SDS/SDS + CFH mixture in all cases indicate spontaneous micelle formation. The  and
and 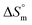 values indicate the presence of both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions amongst the studied components.
values indicate the presence of both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions amongst the studied components.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...