A strategy for preparing non-fluorescent graphene oxide quantum dots as fluorescence quenchers in quantitative real-time PCR
Abstract
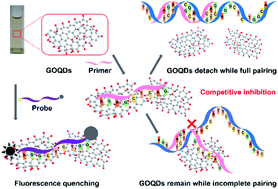
In recent years, graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) have emerged as novel nanomaterials for optical sensing, bioimaging, clinical testing, and environmental testing. However, GOQDs demonstrate unique photoluminescence properties, with GOQDs having quantum limitations and edge effects that often affect the accuracy of the test results in the sensory field. Herein, GOQDs with a large content of hydroxyl groups and low fluorescence intensity were first prepared via an improved Fenton reaction in this study, which introduces a large amount of epoxy groups to break the C–C bonds. The synthesized GOQDs show no significant variation in the fluorescence intensity upon ultraviolet and visible light excitations. We further utilized the GOQDs as fluorescence quenchers for different fluorescent dyes in real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and verified that the addition of GOQDs (5.3 μg ml−1) into a qRT-PCR system could reduce the background fluorescence intensity of the reaction by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) during its initial stage and its non-specific amplification, and improve its specificity. In addition, the qRT-PCR method could detect two different lengths of DNA sequences with a high specificity in the 104 to 1010 copies per μl range. It is of paramount importance to carry out further investigations to establish an efficient, sensitive, and specific RT-PCR method based on the use of GOQD nanomaterials as fluorescence quenchers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...