Sonochemical degradation of pesticides in aqueous solution: investigation on the influence of operating parameters and degradation pathway – a systematic review
Abstract
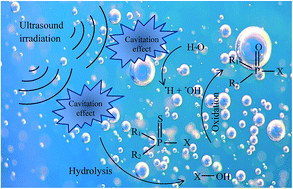
Along with the wide production, consumption and disposal of pesticides in the world, the concerns over their human and environmental health impacts are rapidly growing. Among developing treatment technologies, sonochemistry as an emerging and promising technology for the removal of pesticides in the aqueous environment has attracted the attention of many researchers in recent years. This systematic review presents an extensive study of sonochemical degradation of different types of pesticides from aqueous solution. The influence of various parameters including reactor configurations, initial concentration of pesticide, ultrasonic frequency, intensity of irradiation, bulk solution temperature, operational pH and sonication time on the degradation efficiency has been analyzed. The mechanism of ultrasonic degradation has been discussed, and recommendations for optimum operating conditions have been reported for maximizing degradation efficiency. Additionally, the intensification of ultrasonic cavitation by combining with oxidation processes was overviewed and the main advantages and disadvantages were pointed out, in order to address future studies and promote efficient large-scale operations. As a conclusion, it appears that ultrasonic irradiation can be effectively used for intensification of the degradation of pesticides from aqueous solution.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...