A study on the mechanism of oxidized quinoline removal from acid solutions based on persulfate–iron systems†
Abstract
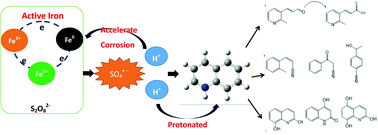
Quinoline (Qu) and its derivatives have been widely regarded as hazardous pollutants in the world because of their acute toxicity to humans and animals, and potential carcinogenic risks. In this study, a novel sulfate radical system co-activated by ferrous and ZVI was developed to remove Qu from acidic solutions. The optimal ratio of ferrous and ZVI in the system and the mechanism of Qu removal from acidic solutions are also explored. The ZVI can initiate activation using hydrogen ions, which are released from the reaction of Fe2+, organics and PS in acidic solutions. This may dramatically improve the overall removal efficiency of Qu. The results indicated that the initial removal rate of Qu increases from 85.8% to 92.9%. The cleavage pathway of Qu is speculated by Frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory and verified by GC/MS analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...