Hollow Au@TiO2 porous electrospun nanofibers for catalytic applications†
Abstract
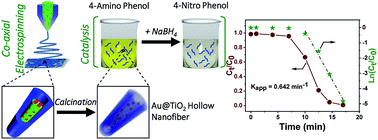
Catalytically active porous and hollow titania nanofibers encapsulating gold nanoparticles were fabricated using a combination of sol–gel chemistry and coaxial electrospinning technique. We report the fabrication of catalytically active porous and hollow titania nanofibers encapsulating gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a combination of sol–gel chemistry and coaxial electrospinning technique. The coaxial electrospinning involved the use of a mixture of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) and titania sol as the shell forming component, whereas a mixture of poly(4-vinyl pyridine) (P4VP) and pre-synthesized AuNPs constituted the core forming component. The core–shell nanofibers were calcined stepwise up to 600 °C which resulted in decomposition and removal of the organic constituents of the nanofibers. This led to the formation of porous and hollow titania nanofibers, where the catalytic AuNPs were embedded in the inner wall of the titania shell. The catalytic activity of the prepared Au@TiO2 porous nanofibers was investigated using a model reaction of catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and Congo red dye in the presence of NaBH4. The Au@TiO2 porous and hollow nanofibers exhibited excellent catalytic activity and recyclability, and the morphology of the nanofibers remained intact after repeated usage. The presented approach could be a promising route for immobilizing various nanosized catalysts in hollow titania supports for the design of stable catalytic systems where the added photocatalytic activity of titania could further be of significance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...