Adhesion and bactericidal properties of nanostructured surfaces dependent on bacterial motility†
Abstract
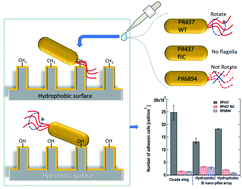
Different nanostructured surfaces have bactericidal properties that arise from the interaction between the bacteria and the nanostructured surface. In this study, we focused on the relationship between bacterial motility and bactericidal properties. The motility of Escherichia coli (E. coli) was tuned by genetic engineering, and four types of E. coli (wild type (WT), lacking flagella, and flagellated with deficient motility or deficient chemotaxis) were used to evaluate the adhesion and bactericidal properties of nanostructured surfaces. Cicada (Cryptotympana facialis) wings and Si nano-pillar array substrates were used as natural and artificial nanostructured surfaces, respectively. Differences in motility and chemotaxis strongly influenced the adhesion behavior and to some extent, the damage to the cell membrane. These results suggest that the bactericidal properties of nanostructured surfaces depend on bacterial motility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...