Detection of biomarkers in body fluids using bioprobes based on aggregation-induced emission fluorogens
Abstract
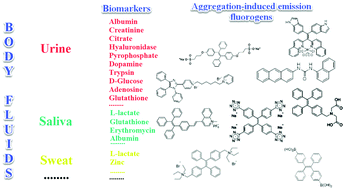
Body fluids (biofluids) are used as a means of examining various biomarkers of health and disease both as a means of rapid diagnosis and monitoring of chronic health conditions. Biomarker detection in non-invasively collected biofluids is considered an easy and rapid method in medical diagnostics. A novel group of bioprobes with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties is being developed for monitoring analytes in biofluids which could facilitate widespread use via commonly available technologies. This review describes the constituents and clinical biomarkers in urine, saliva, and sweat, and the role of currently developed AIE bioprobes that can quantitatively detect disease-related biomarkers in these biofluids. Several applications of AIE bioprobes, such as paper-based strips and POC devices, are currently under development, and offer potential to be realized simply by use with smartphone data capture and analysis and data cloud storage. These low-cost and highly reliable AIE bioprobe applications are beneficial for both early detection of disease and chronic disease management, especially in rural areas and developing countries and may facilitate greater involvement of health care consumers in managing their own care.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Luminogenic bioprobes for personal health technologies and 2020 Materials Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...