Superhydrophobic magnetic core–shell mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with dendritic architecture for oil–water separation†
Abstract
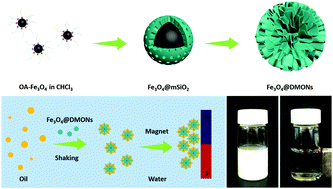
The effective removal of oil contaminants from wastewater, especially dispersed tiny oil droplets, is an emerging technology, yet remains challenging. Core–shell structured nanoparticles with magnetic cores and hydrophobic shells have been explored for oil removal, but the adsorption capacity is unsatisfactory due to the low surface area and smooth surface. Herein, superhydrophobic magnetic core–shell mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles with dendritic architecture (Fe3O4@DMONs) were fabricated in a step-by-step condensation process, which could realize the rapid and efficient separation of dispersed tiny oil droplets from oil-in-water emulsions, giving a separation efficiency of higher than 98.1%. Meanwhile, thanks to the magnetically responsive property, the dispersed Fe3O4@DMONs could be collected simply by applying a magnetic field. In addition, the mesoporous structure as well as the dendritic architecture afforded Fe3O4@DMONs large adsorption capacities for various oils, ranging from 1.37 to 2.04 g g−1. Fe3O4@DMONs showed good reusability with the remaining separation efficiency of 97.9% during five separation cycles for a cyclohexane-in-water emulsion. Furthermore, Fe3O4@DMONs could also adsorb a water-soluble dye in an oil-in-water emulsion with an adsorption efficiency up to 89.4%. Therefore, Fe3O4@DMONs hold promising potential as candidates for the practical purification of industrial wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...