Temperature-sensing luminescent materials La9.67Si6O26.5:Yb3+–Er3+/Ho3+ based on pump-power-dependent upconversion luminescence†
Abstract
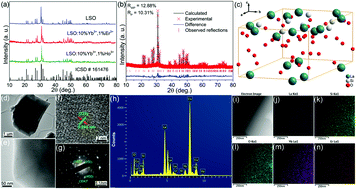
Rare earth ion doped upconversion (UC) luminescent materials could show potential applications in optical temperature sensing. To develop new UC phosphors doped with Yb3+/Ho3+ activators, a series of La9.67Si6O26.5:Yb3+–Er3+/Ho3+ samples were prepared by a solid-state reaction method, and the temperature-sensing properties were evaluated on the basis of the UC spectra. The phase, structure and morphology of the samples were analyzed by XRD, Rietveld refinement and SEM techniques, respectively. The characteristic emission peaks of both Er3+ and Ho3+ appeared and the UC mechanism was discussed. Different strategies for optical temperature sensing were employed for Er3+ and Ho3+. The fluorescence intensity ratio (FIR) for the two green emissions of Er3+ originating from thermally-coupled levels followed the Boltzmann distribution. The effect of the pump power on the sensor sensitivities was investigated in detail. The relative standard deviation and temperature uncertainty were also evaluated. For the Ho3+-activated LSO, the red and green emissions derived from non-thermally-coupled levels were used for temperature sensing. The UC energy transfer processes were discussed in detail to explain the change in the FIR with temperature. High absolute sensitivity was obtained in this phosphor. The above investigations could be instructive in exploring other new luminescent materials for optical temperature sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...