Theoretical insight into the redox-switchable activity of group 4 metal complexes for the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone†
Abstract
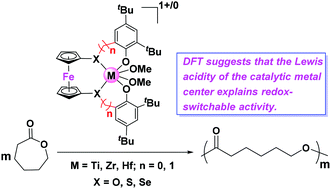
Redox-switchable polymerization has drawn increasing attention, in particular for the ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of biomass-derived monomers. However, an understanding of how the switch determines the observed changes is still limited. In this study, DFT calculations were employed to understand the redox-switchable ROP mechanism of ε-caprolactone catalyzed by group 4 metal complexes bearing [OSSO]-type ferrocene ligands. Our results suggest that two oxidized forms show higher reactivity because of the higher Lewis acidity of their catalytic metal centers in comparison with that of the corresponding reduced states. In one case, however, a lower activity of the oxidized species was observed that is likely due to the increased stability of the substrate-catalyst intermediate leading to a high activation barrier. In addition, other analogous metal complexes were computationally modelled by changing the metal center or modifying the ancillary ligand with different bridging-heteroatoms, and the results provide useful information on the development of new redox-switchable polymerization catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...