Visible-light-driven self-coupling and oxidative dehydrogenation of amines to imines via a Mn(ii)-based coordination polymer†
Abstract
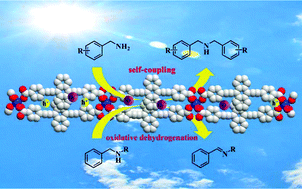
Imines are versatile and valuable organic intermediates in the synthesis of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. The direct synthesis of imines through a one-pot procedure via an oxidative process to reduce energy consumption and waste emission has long been pursued. In this study, we prepared a novel visible-light-responsive coordination polymer with a one-dimensional structure for the direct photocatalytic synthesis of imines in the presence of a green and economical oxidant, molecular oxygen. Photocatalytic experiments suggest that the synthesized coordination polymer is not only efficient for the self-coupling of primary amines to generate homo-coupled imines, but also capable of oxidative dehydrogenation of secondary amines with high selectivity to produce hetero-coupled imines. Mechanistic studies have demonstrated that both photocatalytic reactions depend on reactive oxygen species such as singlet oxygen and superoxide radicals in the system, indicating effective electron and energy transfer from a photoexcited coordination polymer to molecular oxygen. This study not only presents a rare example of a visible-light-driven coordination polymer with a low-dimensional structure capable of direct photocatalytic synthesis of imines, but also demonstrates the great potential of photoactive coordination polymers for organic transformations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...