Defect-induced abnormal enhanced upconversion luminescence in BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ ultrathin nanosheets and its influence on visible-NIR light photocatalysis†
Abstract
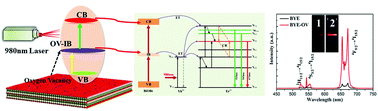
In this work, we design oxygen vacancy-rich BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ (BYE-OV) ultrathin nanosheets, which can effectively enhance UC luminescence by oxygen vacancy engineering. Density functional theory calculations and UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra reveal that the existence of oxygen vacancies leads to the formation of an intermediate band (IB) in the bandgap, which can enhance the light absorption ability and promote electron excitation and bandgap transitions (VB → CB, VB → IB and IB → CB), thereby providing the transfer of abundant electrons from the host to Er3+ ions. As a result, the emission intensity of green and red is exceptionally enhanced by 6.5 and 12 times respectively via introduced oxygen vacancies. Meanwhile, BYE-OV exhibits superior photocatalytic activity for the degradation of RhB under visible-NIR light irradiation. The enhanced activity can be mainly ascribed to enhanced photoabsorption in the visible-NIR region and improved UC luminescence. This work offers a new strategy for a rational design for enhancing UC luminescence, which has potential for applications in visible-NIR light photocatalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...