Highly efficient oxidation of various thioethers catalyzed by organic ligand-modified polyoxomolybdates†
Abstract
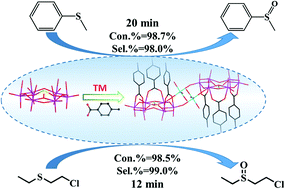
The selective oxidation of thioethers is among the most straightforward and common methods to obtain the synthetic intermediates sulfoxides for application in chemical industry, medicinal chemistry and biology. In this study, we prepared four hybrid compounds, i.e. Cs4[M(H2O)4][PMo6O21(PABA)3]2·nH2O 1–4 (M = Co, Mn, Ni, Zn; PABA = p-aminobenzoic acid), based on carboxylic acid-modified polyoxomolybdates and metal cations with wonderful catalytic performance for the selective oxidation of thioethers. The compounds 1–4 comprise PABA ligand-modified polyoxomolybdates [PMo6O21(PABA)3]3− as building units and the Co2+/Mn2+/Ni2+/Zn2+ cations as linkers to generate novel dimeric architectures. Using compound 1 as a pre-catalyst, methyl phenyl sulfides were nearly entirely converted to sulfoxides with the selectivity of 98% at room temperature within 20 minutes. Satisfactory catalytic effects were also observed in the selective oxidation of various phenyl sulfides with substituent groups; in particular, another typical thioether, i.e. the chemical warfare agent simulant 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide (CEES), could be completely degraded to nontoxic 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfoxide (CEESO) with the selectivity of 99% within 12 minutes at room temperature. These pre-catalysts could be recycled at least 10 times by simple filtration with a negligible decrease in conversion and selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...