Epoxy-functionalised 4-vinylguaiacol for the synthesis of bio-based, degradable star polymers via a RAFT/ROCOP strategy†
Abstract
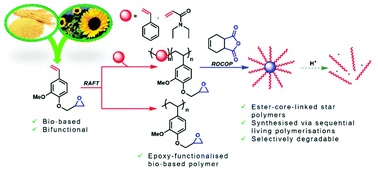
An epoxy derivative of a naturally occuring vinylphenolic compound, 4-vinylguaiacol (4VGEP), was used for the synthesis of a well-defined (Mw/Mn = 1.08–1.14), bio-based styrene-type polymer. Block copolymers of 4VGEP with styrene and diethylacrylamide were also prepared and used as macro-monomers in metal, and metal-free, ring-opening copolymerisation (ROCOP) with cis-4-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboxylic anhydride to form ester cross-linked star polymers in high yields (82–90%), with narrow dispersity (Mw/Mn = 1.27–1.40). Finally, the selective degradation of the ester core of the styrene-based star was achieved under acidic conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...