Soft–hard Janus nanoparticles for polymer encapsulation of solid particulate†
Abstract
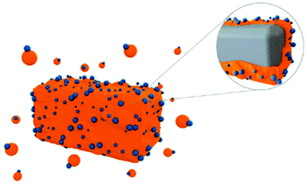
We demonstrate a scalable continuous feed method for the synthesis of polymer Janus nanoparticles with different composition and with different aspect ratios between lobes, including with one hard cross-linked polystyrene lobe and one soft film-forming poly(methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate) (P(MMA-co-BA)) lobe, through reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT)-mediated emulsion polymerization. Snowman shaped particles of size around 40 nm are synthesized through a continuous monomer feeding method, which enables kilogram-scale synthesis of diverse polymer Janus nanoparticles, with a solids content greater than 30%. The Janus nanoparticles with the soft P(MMA-co-BA) lobes spontaneously self-assemble around solid particles in an aqueous phase, forming a thin (5–100 nm) polymer film that completely encapsulates the solid particles. The process is achieved at room temperature and under mild conditions. The film-forming Janus nanoparticles show excellent encapsulation ability for a variety of solid particles, such as organic and inorganic pigments, carbon nanotubes and calcite, without requiring polymerization to be conducted in the presence of the solid particles. When the Janus nanoparticles were used to encapsulate calcite particles in low sheen paints, the encapsulation provided superior stain resistance to the formed paint film.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...