Cross-linking polymerization-induced self-assembly to produce branched core cross-linked star block polymer micelles†
Abstract
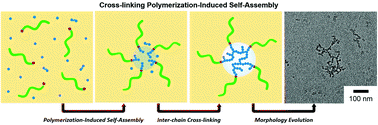
We report polymerization-induced self-assembly via controlled cross-linking copolymerization to produce robust block copolymer micelles with spherical, elongated, and branched shapes. Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) copolymerization of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB) or 1,2-bismaleimidoethane (BMI) as a cross-linker in the presence of a polylactide macro-chain transfer agent (PLA-CTA) was performed in acetonitrile, which is a non-solvent to polystyrene (PS). The addition of the cross-linker accelerates the copolymerization compared to styrene homopolymerization, which leads to the formation of block polymer micelles within a shorter time frame, followed by in situ inter-chain cross-linking. The micelles are virtually identical to the core cross-linked star polymer consisting of a cross-linked polystyrenic core surrounded by a PLA corona. Molecular weights up to more than 1000 kg mol−1 could be obtained with relatively narrow dispersity values (1.1–1.4). In the case of copolymerization with DVB, the micellar morphology changes from spherical to elongated and branched shapes with increasing conversion. The size and morphology of the micelles are retained in a good solvent to PS, suggesting that the in situ cross-linking effectively stabilizes the micellar core. BMI undergoes alternating copolymerization with styrene in the early stage of polymerization and yields spherical micelles exclusively, because the densely cross-linked core seems to prevent further morphological transition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...