Synthesis of biscarboxylic acid functionalised EDTA mimicking polymers and their ability to form Zr(iv) chelation mediated nanostructures†
Abstract
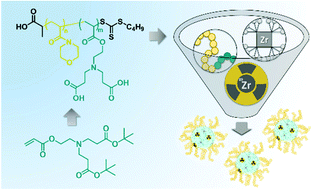
In an effort to design novel chelating polymers, polyacrylates with biscarboxylic acid containing repeating units were synthesised by reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerisation of a new ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) mimicking monomer bearing two carboxylic acids bridged by a tertiary amine group. The monomer presented is accessible in a simple two step strategy and can be polymerised in a controlled fashion enabling the synthesis of defined homopolymers (Đ < 1.3) and the chain extension of a N-acryloyl morpholine chain transfer agent (CTA) to afford block copolymers of tailored composition. Upon deprotection of the carboxylic acid groups, the polymers showed similar pKa values as EDTA and were able to efficiently complex Zr(IV) in aqueous solution. Specifically, complexation studies using block copolymers revealed the formation of defined nanostructures, which were stable in serum containing cell media for at least 24 h. Their negligible cell toxicity and ability to encapsulate 89Zr render the polymers and nanostructures presented suitable candidates for future diagnostic and radiotherapeutic applications in biomedicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...