Metallopolymer-block-oligosaccharide for sub-10 nm microphase separation†
Abstract
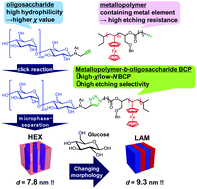
High-χ (where χ is the Flory–Huggins interaction parameter) block copolymers (BCPs) have great potential to achieve ultra-small microphase-separated structures with domain spacings (d) of <10 nm, which in turn are promising for nanofabrication applications. However, when considering their practical application in next generation lithographic processes, sufficient heat resistance and high etching selectivity are also required to attain high-χ BCPs for precise pattern transfer to the substrate. Herein, we report novel high-χ BCPs comprising poly(vinyl ferrocene) (PVFc) and an oligosaccharide (maltotriose and maltohexaose), which simultaneously accomplish small d values, sufficient thermal stability, and high etching selectivity. These novel BCPs, which displayed different architectures and saccharide volume fractions, were synthesized by combining living anionic polymerization and the “click” reaction. Small angle X-ray scattering measurements revealed that PVFc-b-maltohexaose and PVFc-b-(maltotriose)2 formed hexagonal cylinder morphology with d values of ∼8 nm. Furthermore, a lamellar morphology with d values of 9.3 nm was realized by mixing PVFc-b-(maltotriose)2 and glucose. The thermal properties and etching resistance of PVFc and the oligosaccharides were also investigated. As expected, PVFc displayed a high thermal stability (PVFc: Tg, ∼140 °C and decomposition temperature, ∼350 °C) and higher etching resistance than the oligosaccharides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...