Indole-bridged bisphosphine-monoxide palladium catalysts for ethylene polymerization and copolymerization with polar monomers†
Abstract
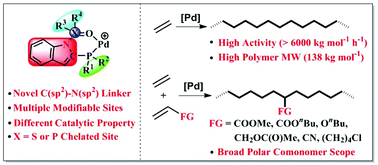
Indole was, for the first time, used to bridge bisphosphine monoxide (BPMO) ligands and thus to construct efficient ethylene (co)polymerization palladium catalysts. By utilizing the indole framework, N(sp2)–C(sp2) linked BPMO-Pd complexes 2a–2g with various P(III) substituents, various P(V)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O substituents, and different X
O substituents, and different X![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O moieties (S
O moieties (S![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O versus P
O versus P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) were synthesized and fully characterized by 1H, 13C, 31P, and 2D-NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. In the presence of NaBArF, these complexes showed completely different activities (0–6210 kg mol−1 h−1) for ethylene polymerization, and generated obviously different molecular weight polyethylenes, with the highest molecular weight being 138 kg mol−1. Preferred palladium catalysts also enabled the copolymerization of ethylene with various commercially available polar monomers such as acrylates, vinyl butyl ether, allyl acetate, acrylonitrile, and 6-chloro-1-hexene to give essentially linear functionalized polyethylenes with comonomer incorporations of 0.3–3.3 mol%. Compared with pioneering C(sp2)–C(sp2) and N(sp2)-bridged analogues, the palladium catalysts in this contribution displayed different correlations between substituents and catalytic properties, which reflects the crucial role of backbone structures and potentially creates new opportunities in catalyst designing.
O) were synthesized and fully characterized by 1H, 13C, 31P, and 2D-NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. In the presence of NaBArF, these complexes showed completely different activities (0–6210 kg mol−1 h−1) for ethylene polymerization, and generated obviously different molecular weight polyethylenes, with the highest molecular weight being 138 kg mol−1. Preferred palladium catalysts also enabled the copolymerization of ethylene with various commercially available polar monomers such as acrylates, vinyl butyl ether, allyl acetate, acrylonitrile, and 6-chloro-1-hexene to give essentially linear functionalized polyethylenes with comonomer incorporations of 0.3–3.3 mol%. Compared with pioneering C(sp2)–C(sp2) and N(sp2)-bridged analogues, the palladium catalysts in this contribution displayed different correlations between substituents and catalytic properties, which reflects the crucial role of backbone structures and potentially creates new opportunities in catalyst designing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...