An optomechanical study of mechanoluminescent elastomeric polyurethanes with different hard segments†
Abstract
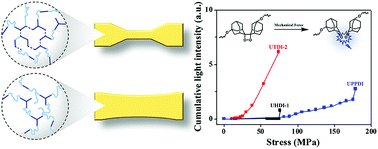
Microphase separation is a unique structural feature of segmented polyurethanes (PUs), and the good mechanical integrity of PUs mainly results from the microphase structures which can be regulated by various hard and soft segments. It is therefore of great importance to study the micro-structures and understand how force is transferred and distributed over this two-phased morphology during mechanical loading. To shed more light on how hard segments influence the microphase structures and the mechanical properties of PUs, we synthesized a series of thermoplastic PUs by choosing different isocyanates as hard segments. Meanwhile, the chemiluminescent mechanophore 1,2-dioxetane is copolymerized into segmented polyurethanes and used as a molecular probe of force. Systematic studies based on optomechanical measurements and DSC, XRD, SAXS and SEM analyses show that the difference in the chemical compositions of the hard segments leads to different microphase separation behaviours in the bulk, and consequently to the unique stress–strain responses and mechanoluminescence behaviors. Benefitting enormously from the chemiluminescent 1,2-dioxetane that allows the study of bond scission events with high sensitivity and resolution in space and time, a detailed molecular picture of how failure occurs in these materials is realized, and the degree of microphase separation can be differentiated more precisely, which is not possible by conventional techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...