A high-performance polycyanurate network derived from 4,4′-biscyanato-2,2′-trifluoromethylbiphenyl†
Abstract
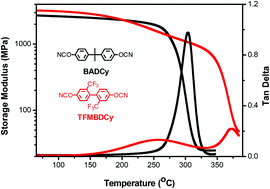
A novel dicyanate, 4,4′-biscyanato-2,2′-trifluoromethylbiphenyl (TFMBDCy), and its thermoset were prepared, and their properties were systematically compared to those of polycyanurates derived from bisphenol A dicyanate (BADCy). The TFMBDCy network exhibited a much higher glass transition temperature, enhanced toughness, reduced water uptake, and improved dielectric properties compared to the BADCy-derived polycyanurate. These improvements resulted from the fluorinated, rigid but non-coplanar architecture of TFMBDCy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...