Shape memory hierarchical AB copolymer networks†
Abstract
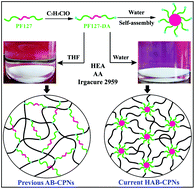
Shape memory polymers (SMPs) have attracted growing attention due to their promising applications in a variety of fields. How to elaborately fabricate polymer networks for SMPs with a combination of high recovery force and perfect shape recovery is a critical issue but remains a challenge. This work reports a novel type of SMP called the shape memory hierarchical AB copolymer networks (HAB-CPNs) that are derived from traditional shape memory AB-CPNs having a structure on a molecular scale only. HAB-CPNs were fabricated by the copolymerization between amphipathic block copolymer micelles (PEO100-PPO65-PEO100:PF127) with vinyl groups on the surface at the nano-level and hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) and acrylic acid (AA) as comonomers. AB-CPNs were prepared by copolymerization of completely soluble PF127 diacrylate, HEA and AA. Meanwhile, the shape memory poly(HEA-co-AA)/PF127 semi-interpenetrating networks (SEMI-IPNs) were prepared with ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as a crosslinker. A comparative analysis of HAB-CPNs, AB-CPNs and SEMI-IPNs, similar in composition but differing in their molecular structure, is performed to explore the impact of different network topologies on the mechanical and shape memory properties. The storage modulus of HAB-CPNs, AB-CPNs and SEMI-IPNs at 30 °C is 2200 MPa, 267 MPa and 32 MPa, respectively. The strain recovery speed of HAB-CPNs, AB-CPNs and SEMI-IPNs is 10.6% min−1, 5.2% min−1 and 2.3% min−1, respectively. The maximum recovery force of HAB-CPNs, AB-CPNs and SEMI-IPNs is 1.83 N, 0.63 N and 0.32 N, respectively. Moreover, HAB-CPNs show excellent cycle performance with just 0.29% cumulative residual strain after 5 consecutive shape memory cycles. High modulus, large recovery force, fast recovery speed, perfect shape recovery and fixity, and excellent cycling stability can be simultaneously achieved in HAB-CPNs. Based on these results, a molecular mechanism of the shape memory effect is proposed by the contrast of HAB-CPNs and AB-CPNs. The high performances of HAB-CPNs can be possibly attributed to the presence of the elastic domains at nanoscale sizes. The proposed mechanism is further verified by detailed stress relaxation analysis. It is anticipated that HAB-CPNs having excellent comprehensive properties will be conducive to the real-world applications of potential SMP devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...