Diblock brush-arm star copolymers via a core-first/graft-from approach using γ-cyclodextrin and ROMP: a modular platform for drug delivery†
Abstract
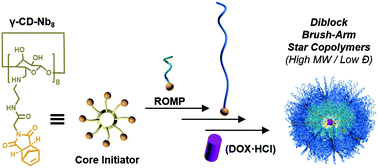
The design and synthesis of a novel multifunctional core initiator based on γ-cyclodextrin (γ-CD) functionalized with eight norbornenes is reported, and a core-first approach to make eight-arm star polymers using ring-opening metathesis polymerization is carried out by grafting-from the initiator using norbornene-functionalized hexaethylene glycol. The living nature of the polymerization was verified through chain extension of the ω-functional arms with norbornene-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG, Mn ≈ 2 kDa) to generate water-soluble diblock brush-arm star copolymers (DBASCs) with high molar masses (Mn,NMR = 187–268 kDa) and low dispersities (Đ = 1.12–1.19). The size of the corresponding star polymers was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering (Dh ≈ 10.0–11.0 nm). The thermal properties (e.g., Tg) of the DBASCs were determined by thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry, the latter of which showed well-ordered materials in the solid state (prominent Tc and Tm peaks). The long-range order and crystallinity of solid-state DBASCs was further supported by well-defined powder X-ray diffraction patterns. Lastly, since γ-CD possesses an order of magnitude greater solubility in water and enhanced drug-binding capabilities compared to that for β-CD, a representative DBASC was evaluated against healthy human umbilical vein endothelial cells (and exhibited low toxicity), and was also investigated as a delivery vehicle for the anticancer drug doxorubicin as its hydrochloride salt (DOX·HCl), resulting in greater potency against MCF-7 breast cancer cells relative to that of the free DOX·HCl treatment. The star polymers reported herein represent a new modular polymeric platform with potential applications in nanostructure self-assembly and drug delivery.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Polymer Chemistry Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...