Deciphering the chemical instability of sphaeropsidin A under physiological conditions – degradation studies and structural elucidation of the major metabolite†
Abstract
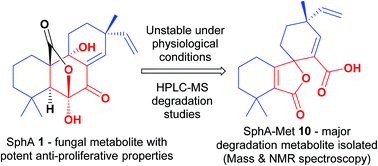
The fungal metabolite sphaeropsidin A (SphA) has been recognised for its promising cytotoxicity, particularly towards apoptosis- and multidrug-resistant cancers. Owing to its intriguing activity, the development of SphA as a potential anticancer agent has been pursued. However, this endeavour is compromised since SphA exhibits poor physicochemical stability under physiological conditions. Herein, SphA's instability in biological media was explored utilizing LC-MS. Notably, the degradation tendency was found to be markedly enhanced in the presence of amino acids in the cell medium utilized. Furthermore, the study investigated the presence of degradation adducts, including the identification, isolation and structural elucidation of a major degradation metabolite, (4R)-4,4′,4′-trimethyl-3′-oxo-4-vinyl-4′,5′,6′,7′-tetrahydro-3′H-spiro[cyclohexane-1,1′-isobenzofuran]-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Considering the reduced cytotoxic potency of aged SphA solutions, as well as that of the isolated degradation metabolite, the reported antiproliferative activity has been attributed primarily to the parent compound (SphA) and not its degradation species. The fact that SphA continues to exhibit remarkable bioactivity, despite being susceptible to degradation, motivates future research efforts to address the challenges associated with this instability impediment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...