Genetic dereplication driven discovery of a tricinoloniol acid biosynthetic pathway in Trichoderma hypoxylon†
Abstract
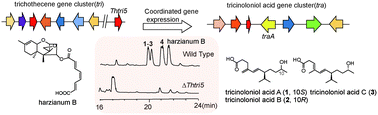
A genetic dereplication approach in combination with differential gene expression led to the discovery of three new sesquiterpenes, tricinoloniol acids (TRAs) A–C (1–3) and the known fusidilactone A (4) from T. hypoxylon. Comparative transcriptomic analysis and targeted deletion identified the biosynthetic route for TRAs. Our results demonstrate an alternative application of the genetic dereplication method for exploring the biosynthesis of cryptic secondary metabolites (SMs), which utilizes the coordinated expression of trichothecene (tri) and tra cluster genes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...