C–H functionalization of quinazolinones by transition metal catalysis
Abstract
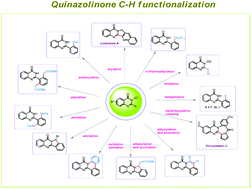
Quinazolinone and its congeners are ubiquitous structural motifs found in numerous natural products due to their wide applications as anticancer, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antifolate and antitumor agents etc. Previously, the synthetic community devoted their efforts towards synthetic approaches but recent years have also witnessed an upsurge in the diversification of this scaffold and its applications. Thus, this review (from 2011 to the beginning of 2020) comprehensively focuses on transition metal catalyzed C–H bond functionalization namely arylation, amination, acetoxylation, amidation, alkylation, alkenylation, alkynylation, halogenation, thiolation, trifluoroethylation etc. of quinazolin-4(3H)-one. Additionally, we also briefly elucidate the plausible mechanistic pathways, scope and limitations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...