Organocatalytic carbon dioxide fixation to epoxides by perfluorinated 1,3,5-triols catalysts†
Abstract
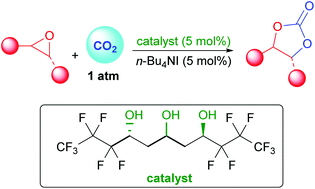
In order to improve epoxides conversion to carbonates by fixation of CO2 a new type of perfluorinated triol catalysts was developed. These simple acyclic scaffolds of enhanced acidity are efficient for catalysis through selective H-bonding activation of the epoxide. In combination with TBAI as co-catalyst, this useful transformation is performed under only 1 atmosphere of CO2 and between 30 to 80 °C. Both the 1,3,5-triol motif and the perfluorinated side chains are crucial in order to observe this epoxide opening under such mild conditions. In addition, the stereochemistry of the starting epoxide can efficiently be conserved during the carbonate formation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis & biocatalysis in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...