The role of phosphopeptides in the mineralisation of silica†
Abstract
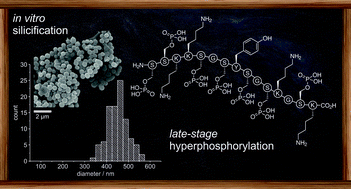
We investigated the silicification activity of hyperphosphorylated peptides in combination with long-chain polyamines (LCPA). The bioinspired in vitro silicification experiments with peptides containing different amounts of phosphorylated serines showed structure–activity dependence by altering the amount and morphology of the silica precipitate. Our study provides an explanation for the considerable metabolic role of diatoms in the synthesis of hyperphosphorylated poly-cationic peptides such as natSil-1A1. The efficient late-stage phosphorylation of peptides yielded a synthetic heptaphosphopeptide whose silicification properties resemble those of natSil-1A1. As opposed to this, unphosphorylated poly-cationic peptides or LCPA require concentrations above 1 mM for silicification. Hyperphosphorylated peptides showed a linear dependence between the amount of dissolved peptides and the amount of precipitated silica in the concentration range below 1 mM. Under mildly acidic conditions and short precipitation times, the concentration of the added LCPA determined the size of the silica spheres.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...