Photoaffinity probes for nematode pheromone receptor identification†
Abstract
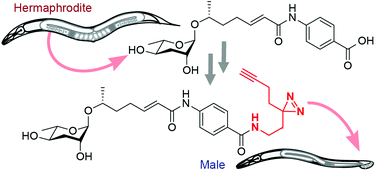
Identification of pheromone receptors plays a central role for uncovering signaling pathways that underlie chemical communication in animals. Here, we describe the synthesis and bioactivity of photoaffinity probes for the ascaroside ascr#8, a sex-pheromone of the model nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Structure–activity studies guided incorporation of alkyne- and diazirine-moieties and revealed that addition of functionality in the sidechain of ascr#8 was well tolerated, whereas modifications to the ascarylose moiety resulted in loss of biological activity. Our study will guide future probe design and provides a basis for pheromone receptor identification via photoaffinity labeling in C. elegans.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...