Synthesis of luminescent core/shell α-Zn3P2/ZnS quantum dots†
Abstract
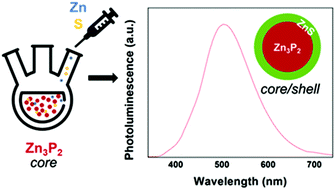
Metal chalcogenide nanoparticles offer vast control over their optoelectronic properties via size, shape, composition, and morphology which has led to their use across fields including optoelectronics, energy storage, and catalysis. While cadmium and lead-based nanocrystals are prevalent in applications, concerns over their toxicity have motivated researchers to explore alternate classes of nanomaterials based on environmentally benign metals such as zinc and tin. The goal of this research is to identify material systems that offer comparable performance to existing metal chalcogenide systems from abundant, recyclable, and environmentally benign materials. With band gaps that span the visible through the infrared, II–V direct band gap semiconductors such as tetragonal zinc phosphide (α-Zn3P2) are promising candidates for optoelectronics. To date, syntheses of α-Zn3P2 nanoparticles have been hindered because of the toxicity of zinc and phosphorus precursors, surface oxidation, and defect states leading to carrier trapping and low photoluminescence quantum yield. This work reports a colloidal synthesis of quantum confined α-Zn3P2 nanoparticles from common phosphorus precursor tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphine and environmentally benign zinc carboxylates. Shelling of the nanoparticles with zinc sulfide is shown as a method of preventing oxidation and improving the optical properties of the nanoparticles. These results show a route to stabilizing α-Zn3P2 nanoparticles for optoelectronic device applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...