Photoacoustic generation of intense and broadband ultrasound pulses with functionalized carbon nanotubes
Abstract
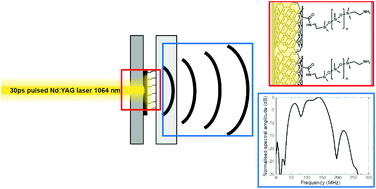
Carbon nanotubes (CNT) functionalized with siloxane groups were dissolved in polystyrene/tetrahydrofuran to produce thin films that generate broadband and intense ultrasound pulses when excited by pulsed lasers. These films absorb >99% of light in the visible and near-infrared and show no signs of fatigue after thousands of laser pulses. Picosecond laser pulses with fluences of 50 mJ cm−2 generate photoacoustic waves with exceptionally wide bandwidths (170 MHz at −6 dB) and peak pressures >1 MPa several millimeters away from the source. The ability to generate such broadband ultrasound pulses is assigned to the ultrafast dissipation of heat by CNT-siloxanes, and to the formation of very thin photoacoustic sources thanks to the high speed of sound of polystyrene. The wide bandwidths achieved allow for axial resolutions of 8 μm at depths less than 1 mm, similar to the resolution of histology but based on real-time non-invasive methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...