Molecular gold strings: aurophilicity, luminescence and structure–property correlations
Abstract
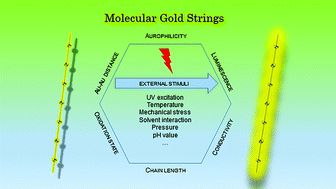
This review covers the compound class of one-dimensional gold strings. These compounds feature a formally infinite repetition of gold complexes as monomers/repeating units that are held together by aurophilic interactions, i.e. direct gold–gold contacts. Their molecular structures are primarily determined in the solid state using single crystal X-ray diffraction. The chemical composition of the employed gold complexes is diverse and furthermore plays a key role in terms of structure characteristics and the resulting properties. One of the most common features of gold strings is their photoluminescence upon UV excitation. The emission energy is often dependent on the distance of adjacent gold ions and the electronic structure of the whole string. In terms of gold strings, these parameters can be fine-tuned by external stimuli such as solvent, pH value, pressure or mechanical stress. This leads to direct structure–property correlations, not only with regard to the photophysical properties, but also electric conductivity for potential application in nanoelectronics. Concerning these correlations, gold strings, consisting of self-assembled individual complexes as building blocks, are the ideal compound class to look at, as perturbations by an inhomogeneity in the ligand sphere (such as the end of a molecule) can be neglected. Therefore, the aim of this review is to shed light on the past achievements and current developments in this area.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...