Comparative electron and photon excitation of localized surface plasmon resonance in lithographic gold arrays for enhanced Raman scattering†
Abstract
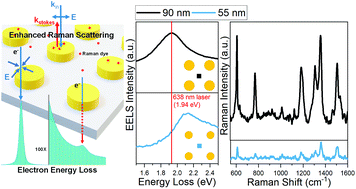
The ability to tune the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of nanostructures is desirable for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), plasmon-assisted chemistry and other nanophotonic applications. Although historically the LSPR is mainly studied by optical techniques, with the recent advancement in electron monochromators and correctors, it has attracted considerable attention in transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Here, we use electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) in a scanning TEM to study individual gold nanodiscs and bowties in lithographic arrays with variable LSPRs by adjusting the size, interspacing, shape and dielectric environment during the nanofabrication process. We observe the strongest Raman signal enhancement when the LSPR frequency is close to the incident laser frequency in Raman spectroscopy. A simplified harmonic oscillator model is used to estimate SERS enhancement factor (EF) from EELS, bridging the connection between electron and photon excitation of plasmonic arrays. This work demonstrates that STEM–EELS shows promise for revealing the contributions of specific LSPR modes to SERS EF. Our results provide guidelines to fine-tune nanoparticle parameters to deliver the maximum signal enhancement in biosensing applications, such as early cancer detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...