Preclinical evaluation of platinum-loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in an embryonic zebrafish xenograft model†
Abstract
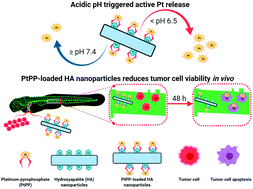
Hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles are commonly used as building blocks in the design of bone-substituting biomaterials. Recently, these nanoparticles have been considered for the treatment of metastasis disease, since their pH-dependent dissolution behavior allows for precise tuning of release kinetics of loaded cargo. Herein we show that the capacity of drug-loaded nanoparticles stabilized with citrate ions reduce cancer cell survival in an embryonic zebrafish xenograft model. In particular, in vitro studies demonstrate that PtPP-loaded HA nanoparticles exhibit anti–proliferative activity against breast cancer cells at reduced pH. In vivo studies using an embryonic zebrafish xenograft model reveal that PtPP co-delivered with human breast cancer cells strongly reduce cancer cell survival. Similarly, co-injection of breast cancer cells with citrate-functionalized and PtPP-loaded HA nanoparticles into zebrafish significantly reduces survival of cancer cells due to release of chemotherapeutically active kiteplatin species. These results demonstrate the preclinical efficacy of drug-loaded nanoparticles against human breast cancer cells in a xenogenic embryonic in vivo model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...